Analysis of urban area resilience combating climate changes case study in Magelang urban area, Central Java, Indonesia
 Author: Mujio, S Nurisjah, B Nailufar, L Aderina, D Siddiq, O Rusdiana, and Y Setiyaningsih
Author: Mujio, S Nurisjah, B Nailufar, L Aderina, D Siddiq, O Rusdiana, and Y Setiyaningsih
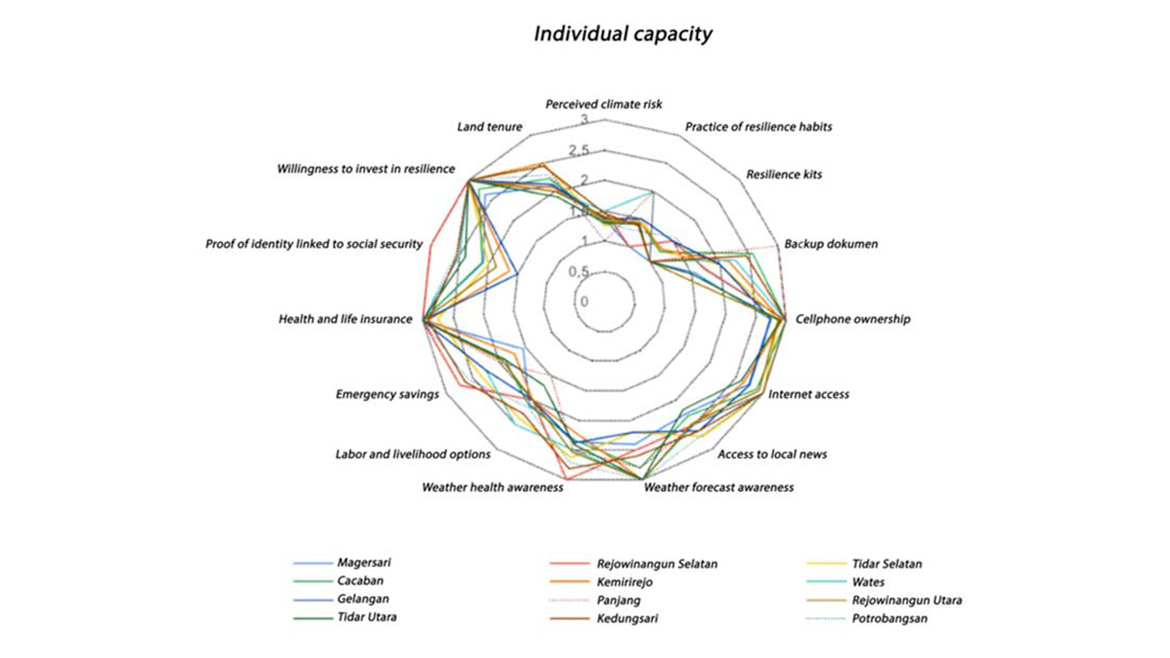
Abstract: The influence of climate change has become a global concern that is increasingly felt by people around the world, including Indonesia. Climate change has an impact on various sectors, such as the food sector (agriculture, fisheries, marine), health, the environment, water resources, and many more. Urban areas are one of the vulnerable areas affected by climate change. In anticipating climate change through adaptation and mitigation efforts in a city’s resilience to current and future climate variability is crucial for an urban area. Based on data from the Indonesian Disaster Risk Index (IRBI) for 2022, Magelang City is included in the medium category. Research on urban resilience analysis in the context of mitigating the consequences of climate change is carried out as a basis for developing urban adaptation/mitigation strategies. This research was carried out with the aim of identifying and determining indicators of city resilience to climate change and carrying out a vulnerability analysis of each location/region potentially affected by climate change. The indicators used in the research are the Urban Community Resilient Assessment (UCRA) Indicators. UCRA is an indicator for measuring urban resilience developed by the World Research Institute (WRI). There are three Indicator Categories developed by UCRA, namely urban vulnerability, Community Resilience, and Community Preparedness. In Magelang City, the most vulnerable indicators of urban vulnerability are the poor population and access to urban services. In analyzing community resilience, the indicators that need to be considered are the early warning system and government support. Meanwhile, the individual capacity that needs to be considered is increasing readiness to face climate risks and economic resources are important.
Proceeding URL: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/1359/1/012064